

The tidal stress experienced over one orbit is referred to as the "diurnal" stress.

Thus, is makes one revolution around Jupiter every Europa day. It has a 3.55 day orbital period and rotation period, so the same side of Europa always faces Jupiter. For every revolution Europa makes around Jupiter it also completes one rotation.
Orbital Resonances of Io, Europa, and Ganymede.Įuropa is locked into a synchronous rotation around Jupiter, just like our Moon is around the Earth. In addition, Io and Ganymede change their distance with respect to Europa and also introduce a tidal stress.įigure 4. This causes a change in the tidal force on the moon. Since Europa does not have a perfectly circular orbit, its distance from Jupiter changes. A perfect circle has an eccentricity of 0, an elliptical orbit has an eccentricity between 0 1 is a hyperbolic orbit. Eccentricity is a measure of how much an orbit deviates from a perfect circle. This resonance forces Europa to have an eccentricity of e = 0.01 (Greenberg 1981, Peale 1986). This is illustrated in the diagram below (Figure 4). For every orbit Ganymede completes, Europa completes two and Io completes four. Table 1 shows that the first three Galilean moons are locked in a 4:2:1 orbital resonance. The change in tidal force (also known as tidal stress) occurs because of the orbits of Io, Europa, and Ganymede. There is enough tidal heating occurring in Europa to keep its interior warm and the moon to stay geological activity, even though it is smaller than our own Moon. This is becuase stretching and flexing induce frictional heating, similar to rubbing your hands together on a cold day. However, if the band is repeatedly stretched and flexed, heat will be generated. A band that is stretched and left stretched will not generate heat. This can be imagined if you take a rubber band and stretch it repeatedly. In order for heating to occur, the tidal force must change. However, it is not tidal force alone that causes tidal heating within a body.
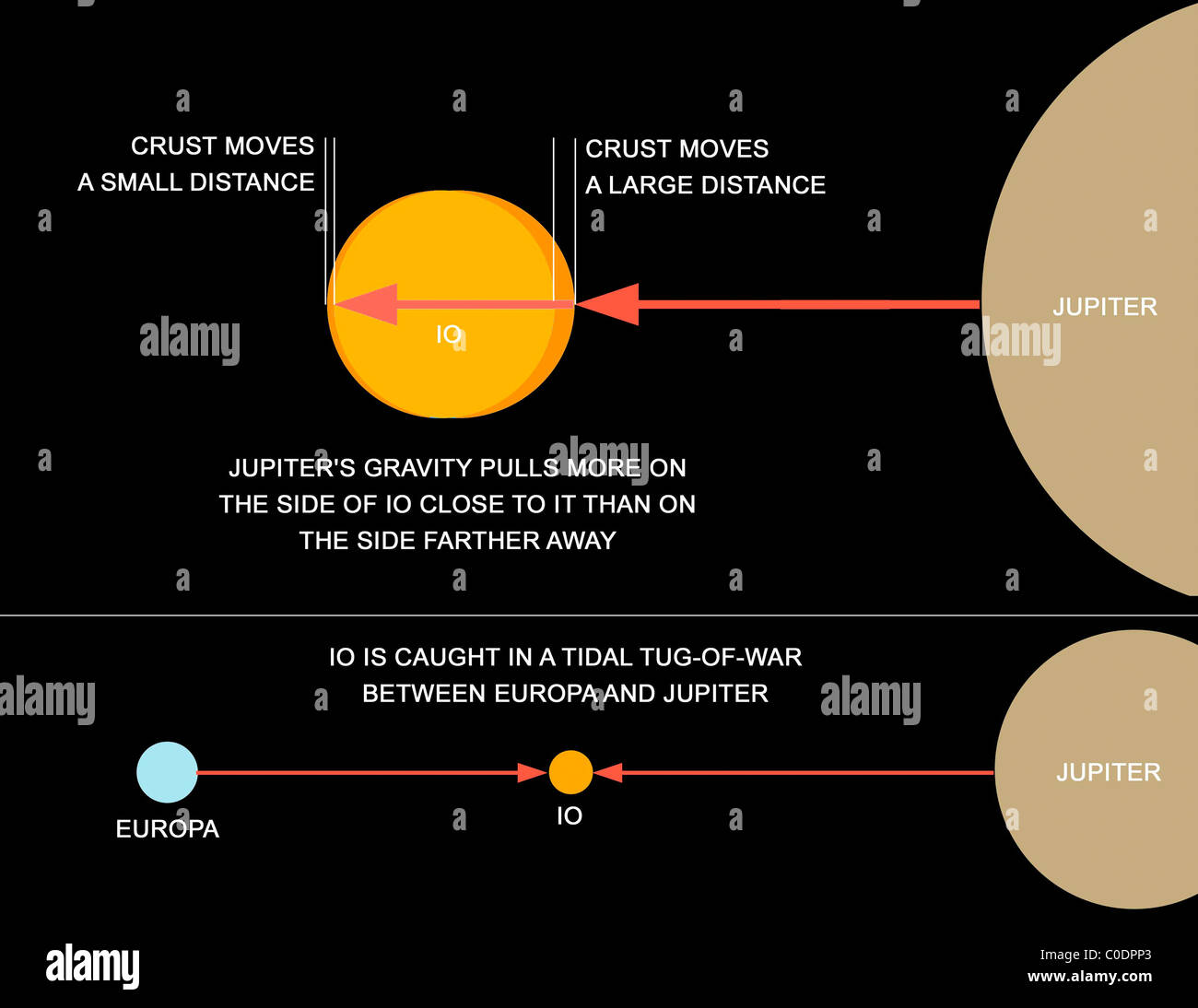
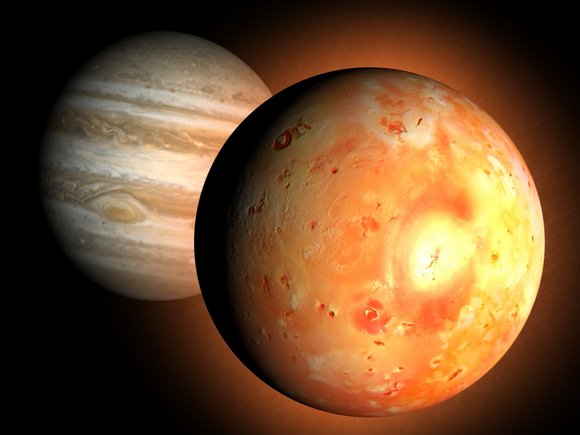
It can be seen that larger moons have greater tidal forces across them. The difference in these two forces is the tidal force felt across Europa: The force felt on the side facing away from Jupiter is: The magnitude of force felt on the side of Europa facing Jupiter is: Since the front face of Europa is closer to Jupiter than the far side, it will feel a greater gravitational force. Tidal force is the differential gravitational force felt across a body. It can be seen that as the distance between the two bodies decreases, the force increases as r 2, and as the mass of the bodies increase the force also increases. Where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the more massive body (Jupiter), m is the mass of the less massive body (Europa), and r is the distance of the two bodies. The magnitude of gravitational force is defined as: The reason for its continued activity is due to tidal heating - a continual flexing and stretching of the Europa caused by the shape of its orbit and gravitational pull from Jupiter, Io, and Ganymede. However, Europa is smaller than our Moon (Table1), yet it is still geologically active. Due to its size, our Moon has had enough time to radiate its heat into space, causing its interior to cool, prohibiting geological activity. It is interesting to see moons in our solar system that are so geologically active while our own Moon is not.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
